Brayton cycle: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Image:Split-brayton-cycle-Ts.png|400px|thumb|none|T-s diagram for the split Brayton cycle]] | [[Image:Split-brayton-cycle-Ts.png|400px|thumb|none|T-s diagram for the split Brayton cycle]] | ||
== | == Regenerative Brayton cycle == | ||
[[Image:Brayton-regen-cycle-config.png|400px|thumb|none|Regenerative Brayton cycle configuration (Figure: Rachel Hogan)]] | |||
This cycle is implemented in the model <tt>brayton_regen</tt>, contained in the file {{src|models/johnpye/brayton_fprops.a4c}}. The T-s diagram of the cycle in our default configuration is shown below: | |||
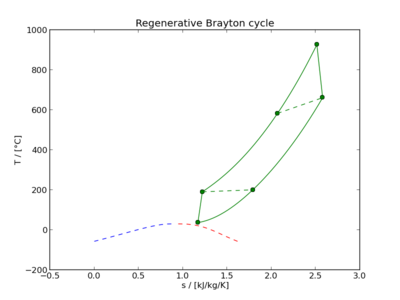
[[Image:Brayton-regen-Ts.png|400px|thumb|none|T-s diagram for the regenerative Brayton cycle]] | |||
{{incomplete}} | {{incomplete}} | ||
[[Category:Examples]] | [[Category:Examples]] | ||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
[[Category:Energy systems]] | [[Category:Energy systems]] | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 13 March 2013
The Brayton cycle the basic thermal power cycle implemented in gas turbines. ASCEND provides support for modelling Brayton cycles with a range of models of increasing complexity.
The models are provided in the file models/johnpye/brayton.a4c
See also Combined-cycle gas turbine
Split Brayton Cycle
This cycle has been identified as highly efficient when the working gas is supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2). The configuration is shown below.

The model brayton_split_co2, contained in the file models/johnpye/brayton_split.a4c, implements this cycle. The T-s diagram of the cycle in our default configuration is shown below:

Regenerative Brayton cycle
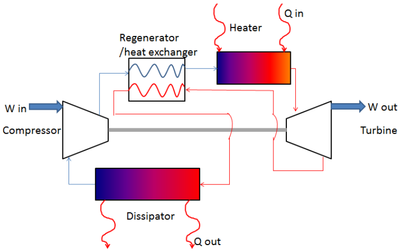
This cycle is implemented in the model brayton_regen, contained in the file models/johnpye/brayton_fprops.a4c. The T-s diagram of the cycle in our default configuration is shown below: